The qui tam whistleblower, not the qui tam whistleblower’s counsel, has standing to request attorneys’ fees under the FCA. Furthermore, the general rule is that these fees are paid to the qui tam whistleblower not the qui tam whistleblower’s attorney.
What is a qui tam lawsuit?
Feb 14, 2020 · Who Pays for Attorney Fees in Qui Tam Cases? The Contingency Fee. When you meet with an attorney for the first time to review your case, that consultation will... Filing the Case. If you decide to start a qui tam case without the help of an attorney, it will still cost you very... If the Government ...
What is the FCA qui tam law?
For example, if the government were to intervene and settle a qui tam case for $1 million, and it agreed to pay out a 20% relator’s share, the whistleblower would receive $200,000 of the $1 million settlement. As part of the engagement process, the lawyers and client will have agreed upon a percentage of the relator’s share that will be paid to the lawyer as its contingency fee.
Where to file a qui tam complaint in federal court?
The rate is adjusted to fully compensate the firm’s attorneys based on their expertise and years of experience beyond the 20-year floor set by the Matrix. See Purdue v. Kenny, 130 S.Ct. 1662 (2010). For purposes of all attorney fee billings, including obtaining fees in fee-shifting cases, our firm uses the Laffey Matrix.
How long does a qui tam case stay under seal?
Jan 19, 2016 · In the event you do need to pay costs, it usually comes directly from the money recovered by the lawsuit. Here is an overview of how the process usually works: The Start: Filing a False Claims Act Case. The costs to get started on an FCA or qui tam case are relatively small, including a small federal filing fee and possible administrative expenses. However, when you …
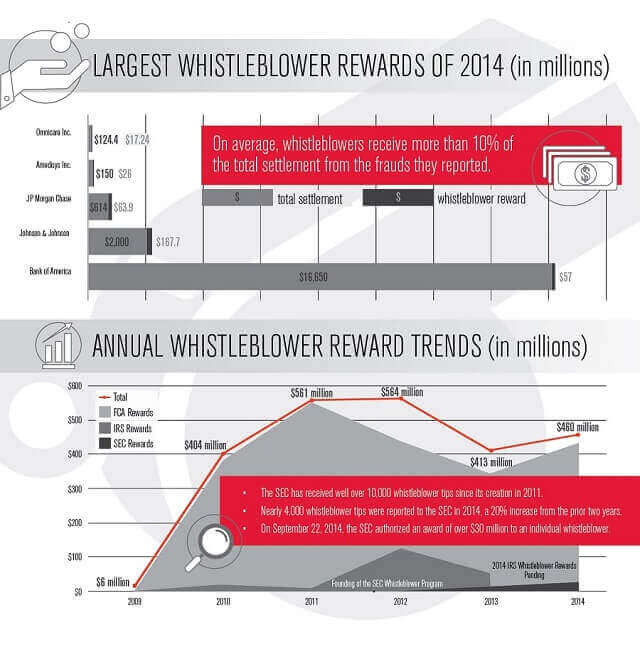
Who typically pays for attorney's fees in the United States?
What Are Attorney's Fee Awards? Attorney's fee awards refer to the order of the payment of the attorney fees of one party by another party. In the U.S., each party in a legal case typically pays for his/her own attorney fees, under a principle known as the American rule.
What type of award is a qui tam relator eligible to receive for bringing a case in which the government intervenes?
The False Claims Act authorizes qui tam lawsuits to assist the government in prosecuting cases to recover damages and penalties for fraud against the government. If the case is successful, the relator can earn a whistleblower reward.
What type of award is a qui tam relator eligible to receive?
Whistleblowers (known as “relators” in qui tam lawsuits) are awarded a whistleblower reward based on a percentage of the money recovered by the government when those recoveries are due to a qui tam lawsuit or claims made under the SEC, CFTC or IRS whistleblower programs.
What percentage of False Claims Act cases are successful?
About 80 percent of all fraud cases won under the False Claims Act are a direct result of whistleblower lawsuits. Whistleblower awards under the Federal law have averaged 17% of recoveries. Whistleblowers usually compensate their attorneys by sharing the award.
How is a qui tam lawsuit different than most other civil cases?
Qui tam lawsuits are civil suits that are brought by whistleblowers under the False Claims Act to stop many different types of fraud against the government. Some types of fraud that may give rise to a qui tam lawsuit include: Knowingly presenting to the federal government a fraudulent claim for payment.Oct 18, 2021
What is a qui tam realtor?
Definition. In a qui tam action, a private party called a relator brings an action on the government's behalf. The government, not the relator, is considered the real plaintiff. ... If successful, a relator in a False Claims Act qui tam action may receive up to 30% of the government's award.
Do whistleblowers get paid in South Africa?
Conclusion In the Republic of South Africa, whistleblowers are only compensated for occupational detriment suffered and not for blowing the whistle as per the Protected Disclosures Act.
Do federal whistleblowers get paid?
A whistleblower reward is a monetary incentive provided by the government to reward a whistleblower's disclosure of original information that leads to a successful enforcement action. Whistleblowers can receive an award of up to 30% of the monetary sanctions collected in a succesful enforcement action.Jan 8, 2022
Do whistleblowers get paid UK?
Compensation for whistleblowers Further compensation available for injury to feelings due to any victimisation is between £900 – £45,600 (from April 2021). This element is similar to that in discrimination claims.
What is the average whistleblower settlement?
The mathematical average of the total recoveries (settlements and judgments) for this time period is approximately $3.3 million, with an average whistleblower award of $562,000.
What are the penalties for violating the False Claims Act?
Violations under the federal False Claims Act can result in significant fines and penalties. Financial penalties to the person or organization includes recovery of three times the amount of the false claim(s), plus an additional penalty of $5,500.00 to $11,000.00 per claim.
What is an example of a violation of the False Claims Act?
Examples of practices that may violate the False Claims Act if done knowingly and intentionally, include the following: Billing for services not rendered. Knowingly submitting inaccurate claims for services. Taking or giving a kickback for a referral.
What is the FCA in qui tam?
The FCA provides that whistleblowers may be eligible to recover legal costs from the defendant in addition to the reward itself. These expenses can include attorney fees and other costs associated with trying the case.
What does a whistleblower attorney do?
A whistleblower attorney usually performs an initial review of a case for free. Once the attorney decides to take the case, you can retain the attorney on a contingency basis. This arrangement means that you will pay the attorney only if the case is successful and you receive a reward from the government. An attorney who works on a contingency basis pays all expenses needed to represent you. These expenses include the costs of hiring expert witnesses, traveling, and completing documentation. They are also entitled to seek reimbursement of these expenses from the defendant if the case is successful.
How much does a whistleblower get in a qui tam case?
If the government intervenes, the qui tam whistleblower is entitled to receive fifteen to twenty-five percent of the proceeds in a qui tam case, subject to the qui tam whistleblower’s noninvolvement in the alleged wrongdoing and lack of public disclosure issues. The amount the qui tam whistleblower receives depends upon the extent to which the person substantially contributed to the prosecution of the action. The Senate factors provided by the legislative history of Section 3730 and the Department of Justice (“DOJ”) Guidelines both provide factors, which courts may take into account when determining the qui tam whistleblower’s share.
How to increase the Qui Tam whistleblower's share?
The following factors are recommended to increase the qui tam whistleblower’s share: 1) qui tam whistleblower reported the fraud promptly; 2) upon learning of the fraud, the qui tam whistleblower attempted to stop it, or reported it to a supervisor or the Government; 3) the qui tam filing or investigation caused the defendant to stop the fraudulent practices; 4) the complaint warned the Government of a safety issue; 5) the complaint exposed a nationwide practice; 6) qui tam whistleblower provided extensive, first-hand details of the fraud to the Government; 7) the Government had no previous knowledge of the fraud; 8) qui tam whistleblower provided substantial assistance during the investigation and pretrial phases of the case; 9) excellent quality of qui tam whistleblower’s witness testimony; 10) qui tam whistleblower’s counsel provided substantial assistance to the Government; 11) qui tam whistleblower and counsel supported and cooperated with the Government during the entire proceeding; 12) the case went to trial; 13) the FCA recovery was relatively small; and 14) there was a substantial, adverse impact on qui tam whistleblower as a result of filing the complaint.
What is the purpose of the FCA?
The FCA provides that if the Government chooses to seek an alternate remedy for its losses instead of proceeding under the FCA. The qui tam whistleblower who originally brought the action is entitled to the same rights as if the Government had proceeded with the action under the FCA. Therefore, if the Government chooses to pursue an alternate ...
How much of the proceeds of a whistleblower's case is left to the court?
In a case where the Government does not intervene, Section 3730 (d) (2) provides the qui tam whistleblower with twenty-five to thirty percent of the proceeds; the actual amount within this range is left to the court’s discretion. When determining the final amount of the qui tam whistleblower’s share, courts consider the same type of factors as those considered when the Government does intervene.
Can a whistleblower recover attorney fees?
Furthermore, the general rule is that these fees are paid to the qui tam whistleblower not the qui tam whistleblower’ s attorney. A qui tam whistleblower may not request fees unless there is an attorney-client relationship, even if the qui tam whistleblower is an attorney.
Who is the whistleblower law firm?
Since its founding in 1988 the whistleblower law firm of Kohn, Kohn, and Colapinto has dedicated thousands of hours providing free or “ pro bono ” legal services on behalf of whistleblowers and whistleblower advocacy organizations.
Do whistleblowers get paid hourly?
Whistleblowers are not charged an hourly fee. Instead, we agree to represent whistleblowers in exchange for obtaining a percentage of a final recovery. In these cases, our clients are not required to pay any upfront attorney’s fees and owe us nothing if we are unable to obtain a recovery or award on their behalf.
The Start: Filing a False Claims Act Case
The costs to get started on an FCA or qui tam case are relatively small, including a small federal filing fee and possible administrative expenses. However, when you file a qui tam case, your lawyer is likely to ask you to agree to something called a contingent fee arrangement.
Government Intervention: Whether Uncle Sam Decides to Join Your Case
FCA claims are a bit different than the normal court case or civil litigation. When you file, you inform the government of your case, but not the defendant. You must inform them of the particular facts surrounding your case, so the government can investigate the claims.
More Questions on Whistleblower Attorney Fees?
No problem! Contact the skilled attorneys at Bothwell Law Group by calling 770.643.1606, and ask about how we handle whistleblower attorney fees.
The Legislative History
Usually, the awarding of fees in litigation is governed by the so-called “American rule” which holds that each party bears the cost of its own attorneys’ fees.
Parsing the Language
It is important to remember that § 3730 (d) (1) & (2) provides for the mandatory award of three categories of expenses. The very language of the provision makes it clear that it is addressing three separate categories of expenditures. See United States ex rel. Lidenthal v. General Dynamics Corp., 61 F.3d 1402, 1413-14 (9th Cir. 1995), cert.
Key Points Established in the Case Law
The best way to appreciate the intricacies of § 3730 (d) (1) & (2) is to dip into the pertinent case authority. Cases interpreting the section, while not extensive at this point, address those issues that would typically arise in litigation. Among the central principles established in the current case holdings are the following:
Conclusions
Whenever defense counsel is facing a qui tam complaint, he should at the outset fully brief the client on the potential additional liability that attaches as a result of § 3730 (d) (1) & (2). Depending upon the nature and complexity of the case, this additional liability may well substantially impact the client’s strategy.
Introduction
While most counsel and defendants in qui tam cases are aware that the False Claims Act (“FCA”) in Section 3730 (d) (2) provides for the mandatory award of attorney’s fees and expenses to successful relators, it is generally not recognized that a corresponding provision can serve as the basis for such an award to prevailing defendants.
Few Courts have Addressed Section 3730 (d) (4)
There are few cases authorities addressing exactly what the reach of Section 3730 (d) (4) may be. These cases, however, can be most helpful to a prevailing defendant in appropriate situations.
The Fleet Financial Group Decision
One of the rare decisions in which prevailing defendants were successful in recovering attorneys’ fees and expenses under Section 3730 (d) (4) is United States ex rel. Stewart v. Fleet Financial Group, et al., Case No. 1:98cv 75, 1999 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 13624 (W.D. Mich. August 31, 1999). The case is informative on several fronts.
Relators Will Argue Fee Awards Are Contrary to Public Policy
Relators often argue that there is a purported general public policy favoring an award of attorneys’ fees only under the most egregious circumstances. A particularly effective rebuttal to this contention is contained in United States ex rel. Herbert v. National Academy of Sciences, No. 90-2568, 1992 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 14063 (D.D.C. Sept.
Strategic Considerations
It is sound strategy to avoid “springing” the concept of attorney’s fees and expenses upon relators by waiting until the conclusion of litigation to alert them to the issue.
Conclusion
Successfully securing the award of attorney’s fees and expenses under Section 3730 (d) (4) almost certainly will prove to be an arduous undertaking which is often doomed to failure.
How long does a qui tam take?
The statute of limitations for a qui tam action is either six years after the date from when a fraud was committed; or three years beyond the date which the United States should be aware of the “material facts,” – but this should not exceed 10 years.
What does "qui tam" mean?
The word qui tam is pronounced “kee tam,” or often also pronounced as “kwee tam,” which means “in the name of the king.”. Under the False Claims Act, qui tam allows persons and entities with evidence of fraud against federal programs or government contracts to file a qui tam lawsuit against the wrongdoer on behalf of the United States Government.
What are the types of fraud?
These types of fraud include: 1 Healthcare Fraud: Medicaid and Medicare Fraud committed by doctors, hospitals and other types of medical care facilities; Unnecessary medical procedures billed to Medicaid or Medicare, such as upcoding; Illegal marketing of drugs by pharmaceutical companies; 2 National Defense Fraud: Defense contract fraud, where funds are shifted from one contract to another to profit, or the intentional inflation of costs; 3 Education & Financial Aid Fraud : For-profit colleges and universities violate the rules of the student loan programs improperly recruiting students to generate income; 4 Bank & Mortgage Fraud : Bankers submitting fraudulent claims for government insurance based on wrongful foreclosures; 5 Underpayments to Government: A reverse false claims action can occur when defendants knowingly make a false statement in order to avoid having to pay the government when payment is otherwise due.
What is the False Claims Act?
The False Claims Act is codified as 31 U.S.C. §§ 3729-33. Section 3729 sets forth anti-fraud requirements of the Act, and 31 U.S.C. 3731 includes the provisions related to filing a qui tam lawsuit. 1.
How much can a whistleblower get?
A False Claims Act whistleblower can receive a whistleblower reward of between 15 and 30 percent of the total recovery the U.S. gets from the defendant. The other award programs offer between 10 and 30 percent, depending on the sanction amount.
When was the False Claims Act created?
The original False Claims Act was created and signed into law by President Abraham Lincoln on March 2 , 1863, at the height of the U.S. Civil War. During the Civil War, there were several contracting scandals in which the government was ripped off.
Do whistleblowers pay attorney fees?
Many whistleblower attorneys work for a “contingency” fee. In a contingency fee case the clients do not pay any attorney’s fees. If the whistleblower loses his or her case, they do not owe the attorney any money. If the whistleblower wins the case, the contingency payment for the attorney is generally between 30% and 40% of the award.
What is above the line deduction?
The above-the-line deduction is available for any action‘‘involving a claim of unlawful discrimination.’’ Of course,many complaints allege multiple claims. Read literally, thislanguage suggests that if oneclaim in a lawsuit qualifies as aclaim of unlawful discrimination, thenall of the legal feesmay be deducted under section 62(a)(20).
What is Section 62(a)(20)?
Section 62(a)(20) was enacted as part of the AmericanJobs Creation Act of 2004. It allows the taxpayer to deductabove-the-line attorney fees and court costs paid by thetaxpayer ‘‘in connection with any action involving a claim ofunlawful discrimination.’’ The term ‘‘unlawful discrimina-tion’’ for the purposes of section 62(a)(20) is statutorilydefined in section 62(e).

Impact of Settlement Before Trial
- Courts differ on the precise impact that settling a qui tam case should have on the qui tam whistleblower’s share. For example, one court, noting that Section 3730(d) makes no distinction for whether the case is settled or tried, awarded the qui tam whistleblower the maximum thirty percent share. In contrast, another court stated that the full share should rarely …
Impact of Government Intervention
- If the government intervenes, the qui tam whistlebloweris entitled to receive fifteen to twenty-five percent of the proceeds in a qui tam case, subject to the qui tam whistleblower’s noninvolvement in the alleged wrongdoing and lack of public disclosure issues. The amount the qui tam whistleblower receives depends upon the extent to which the person substantially contribut…
Senate Factors
- Congress set out three guidelines, known as “Senate Factors,” as a guide for the judiciary to use when determining qui tam whistleblower recovery. The “Senate Factors” are: 1) the significance of the information; 2) the contribution of the person bringing the action to the result obtained; and 3) whether the information was previously known to the government.
Department of Justice Guidelines
- The DOJ Guidelines suggest factors to consider both in favor of increasing and decreasing the qui tam whistleblower’s share. The following factors are recommended to increase the qui tam whistleblower’s share: 1) qui tam whistleblower reported the fraud promptly; 2) upon learning of the fraud, the qui tam whistleblower attempted to stop it, or reported it to a supervisor or the Go…
Impact of Public Disclosure
- The FCA limits the qui tamwhistleblower’s share to no more than ten percent if the court finds that the qui tam action is based primarily on publicly available information.
Effect of Government Non-Intervention
- In a case where the Government does not intervene, Section 3730(d)(2) provides the qui tam whistleblower with twenty-five to thirty percent of the proceeds; the actual amount within this range is left to the court’s discretion. When determining the final amount of the qui tam whistleblower’s share, courts consider the same type of factors as those considered when the G…
Effect of Qui Tam Whistleblower Involvement in The Wrongdoing
- If the court finds the qui tam action was brought by a person who planned and initiated the alleged violation, the court may reduce the amount of the qui tam whistleblower’s share to the extent it considers appropriate. This reduction applies whether or not the government intervened in the action. In determining the appropriate reduction, the FCA requires the court to take into ac…
Qui Tam Whistleblower’S Share If The Government Pursues Alternative Remedies
- The Government may pursue an alternate remedy even if it declines to intervene in the qui tam whistleblower’s action. The FCA provides that if the Government chooses to seek an alternate remedy for its losses instead of proceeding under the FCA. The qui tam whistleblower who originally brought the action is entitled to the same rights as if the Government had proceeded w…
Attorney Fees, Costs, and Expenses
- In addition to a share of the recovery, the FCA provides that a qui tam whistleblower may recover attorney fees, costs, and expenses. The qui tam whistleblower, not the qui tam whistleblower’s counsel, has standing to request attorneys’ fees under the FCA. Furthermore, the general rule is that these fees are paid to the qui tam whistleblower not the qui tam whistleblower’s attorney. A …
Popular Posts:
- 1. what kind of attorney handles sexual abuse cases
- 2. how do you sign a document with power of attorney
- 3. what does durable power of attorney allow me to do + sell parents car in michigan
- 4. what to do with in attorney that is taking your money and not completing the job
- 5. how to deal with the attorney general as a creditor
- 6. how much is a u.s. attorney paid
- 7. who is the district attorney of staten island, ny?
- 8. attorney who practices web law
- 9. what is the difference between a living will and a durable healthcare power of attorney
- 10. trump attorney....says who