- A living will lets you state your preferences for medical treatment
- A medical power of attorney lets you choose a person to make your healthcare decisions
- A durable power of attorney remains effective when you’re incapacitated
- Powers of attorney cannot override living wills — the person you granted POA must try to follow your wishes
Can a power of attorney override a living will?
Aug 11, 2016 · How Does a Healthcare Power of Attorney Differ From a Living Will? A healthcare power of attorney is different from a living will, because naming an agent involves designated someone to act for you while a living will allows you to provide advanced instructions for yourself. As the Cleveland Clinic explains: “Living Will Declaration means a legal document that …
What is the power of attorney and living will?
Apr 15, 2017 · One significant difference is that the health-care power of attorney is much more broadly applicable. A living will comes into effect only when the issue is whether to use a life-sustaining treatment to postpone the moment of death or maintain you in a permanent unconscious state.
How to set up a power of attorney for healthcare?
A Power of Attorney grants authority to someone you trust to act on your behalf. Learn more details about each of these essential, but very different, parts of an Estate Plan here. What is a Living Will. Scenarios to Cover in a Living Will. What is a Power of Attorney. Combining Healthcare Directives. What is a Living Will. A Living Will is a formal, legal, written document that you can …
Will, living trust and power of attorney?
A medical power of attorney differs from a living will in that it appoints an individual to act as an agent for the principal and make decisions for them should they become incapacitated. As long as the principal remains conscious, their medical decisions remain theirs to make.
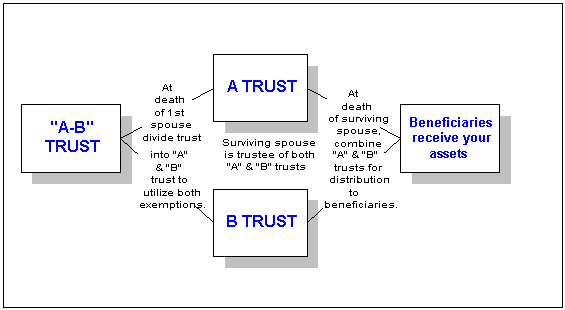
How does a living will differ from the power of healthcare attorney?
At a high level, a Living Will is a legal document that clearly and explicitly states your wishes in regards to medical treatments and decisions. A Power of Attorney grants authority to someone you trust to act on your behalf.
What is the difference between a health care directive and a living will?
So what's the difference between an advance directive and a living will? The short answer is that a living will is a type of advance directive, while “advance directive” is a broad term used to describe any legal document that addresses your future medical care.Aug 5, 2021
What is difference between living will and health care proxy?
A healthcare proxy and a living will both have the same purpose: to see that your medical wishes are expressed and honored, even when you can't do so yourself. You give a medical proxy the authority to make those decisions for you, while a living will sets those wishes out in writing.May 27, 2021
What is the difference between a living will and a durable power of attorney for healthcare quizlet?
A living will is a directive that declares the patient's wishes should the patient become unable to give instruction. A durable power of attorney identifies a person who will make healthcare decisions in the event the patient is unable to do so.
What should be included in a healthcare directive?
What to Include in Your Advance Directive. The name and contact information of your healthcare agent or proxy. Answers to specific questions about your preferences for care if you become unable to speak for yourself. The forms and questions asked vary a bit from state to state.
What does Durable power of attorney mean in medical terms?
Durable power of attorney: A type of advance medical directive in which legal documents provide the power of attorney to another person in the case of an incapacitating medical condition.Mar 29, 2021
What is the difference between a healthcare surrogate and a healthcare proxy?
ELDER LAW UPDATE: COVID-19 FAQs – What is the difference between a Health Care Proxy and a Health Care Surrogate? A Health Care Proxy is the person that will make medical decisions in the event you cannot and do not have a Health Care Surrogate Designation Form.Apr 23, 2020
Can a family member override a healthcare proxy?
Also, no matter what choices you have written on paper, your Health Care Proxy can override any decision and can make choices without regard to any other family member, friend, or medical provider's opinion.Apr 15, 2020
What power does a healthcare proxy have?
A health care proxy, or durable power of attorney for health care, allows you to designate another person as your agent to make health care decisions on your behalf.
What do a living will and a durable power of attorney for health care share in common quizlet?
Both a living will and a durable healthcare POA allow you to choose someone you trust to make certain medical choices on your behalf. You must be at least 18 to create either document and you must be of sound mind. That means no one is allowed to coerce you into making a living will or healthcare power of attorney.
Can power of attorney override will?
A last will and testament and a power of attorney are two of the most common legal documents that authorize another person to take control of your affairs. Because these documents perform very different functions—even coming into effect during different circumstances—a power of attorney doesn't override a will.
What is the purpose of a durable power of attorney for health care Dpoahc )? Quizlet?
What is the purpose of a durable power of attorney for health care (DPOAHC)? A DPOAHC is a legal document in which the patient appoints a health care proxy who will make health care decisions for the patient if the patient loses this ability.
Popular Posts:
- 1. what can an attorney do for a not turn on left tickets
- 2. how to amend a durable power of attorney in california
- 3. how complete is the background criminal check that my attorney does for me?
- 4. what kind of attorney do i need to make up a property agreement
- 5. can i get in trouble if my attorney bills his time when i bill for patalegal work
- 6. how much does a civil rights attorney make
- 7. power of attorney sample how to fill it up
- 8. what is cost for attorney to do an estate plan in ny state
- 9. how to make your own power of attorney
- 10. who is cayuga county's attorney now?