For example, if you write "***PRIVILEGED AND CONFIDENTIAL***" in the subject line of your email, it's less likely that anyone would miss it. Many attorneys add a disclaimer to the "signature" block of their emails stating that the material in their emails is subject to attorney-client privilege.
How to label document attorney client privilege?
· Common examples of privilege waivers: Forwarding a privileged email communication to a third party. Sharing (in writing or orally) the substance of the lawyer’s advice. “My lawyer says we can’t do that” can be a waiver. Including privileged materials in a data room. Sharing privileged materials with an outside auditor, lender, or certain advisors.
What is protected by attorney client privilege?
· Write smart regardless of your level of confidence that the attorney-client privilege applies. You should always anticipate that anything you write may ultimately end up in the hands of your adversaries. Know the applicable laws in your state regarding the attorney-client privilege. Everyone on the legal team should know and understand the basics.
What is client and attorney privilege?
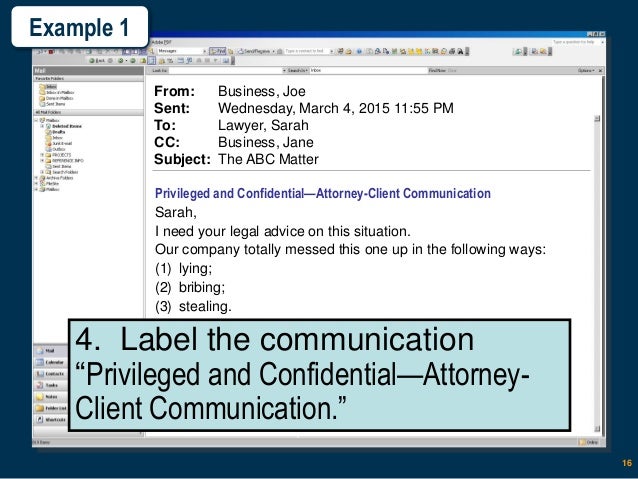
· Rule 3: Label the top of the communication or the subject line of an email: "Privileged and Confidential: Attorney-Client Privileged Communication." This notice should be prominent and easily ...
Does attorney client privilege apply prospective clients?
Examples of Attorney-Client Privilege Documents in a sentence. Attorney-Client Privilege Documents 58, 62, 63, 122, 153, 156, and 164 Plaintiffs contend that, based on their review of the privilege log, each of these documents relate to the subject matter for which the Strausser defendants concede they have waived any applicable attorney-client protection.
How do I label a document attorney-client privilege?
To be safe put "Attorney-Client Communication", "Privileged and Confidential" or "Attorney Work Product" in the subject of the e-mail, or on privileged documents.
How do you abbreviate attorney-client privilege?
We also use the acronym ACP for attorney-client privilege.
How do you mark an email as attorney-client privilege?
When sending an email that contains legal advice or a request for legal advice, apply a label that make this clear, such as “Privileged & Confidential” and/or “Attorney-Client Communication.” Such a label will not be dispositive, but it indicates the intention of the sender to seek legal advice.
How do you determine if a document is privileged?
Parties must identify: “(a) the date of the communication, (b) the parties to the communication (including their names and corporate positions), (c) the names of the attorneys who were parties to the communication, and (d) the subject [matter] of the communication sufficient to show why the privilege applies.” Unisuper ...
What does ACP mean in legal terms?
Attorney-Client Privilege (legal ethics) ACP.
How do you mark something privileged and Confidential?
Rule 3: Label the top of the communication or the subject line of an email: "Privileged and Confidential: Attorney-Client Privileged Communication." This notice should be prominent and easily viewable as soon as someone receives the communication.
How do I mark an email as Confidential and privileged in Outlook?
Mark an email message as private or confidential in OutlookCreate a new email message.In the Message window, please click File > Info > Properties. ... In the Properties dialog box, please select Private or Confidential from the Sensitivity drop-down list. ... Compose your email message, and click Send button to send it.
What is an example of privileged communication?
Examples of privileged communication recognized in many legal jurisdictions include: Attorney-client privilege, involving private conversations between lawyers and those they represent. Spousal conversations, as in the case where one spouse cannot be compelled to testify against another.
What are privileged documents in document review?
Privileged documents are those which need not be disclosed to the other party, neither before nor after the commencement of the trial. Their non-disclosure is allowed by the law itself and the party having such privilege can claim it as a legal right of not disclosing the document containing the concerned information.
What are non privileged documents?
Non-Privileged Documentation . Means documentation, whether hard copy or electronic, which is not subject to any legal privilege preventing its discovery and/or disclosure in a legal proceeding.
What is legally privileged material?
Legal advice privilege covers confidential communications between a client and its lawyers, whereby legal advice is given or sought. Privilege attaches to all material forming the lawyer-client communications, even if those documents do not expressly seek or convey legal advice.
What is privileged attorney?
What is privileged? The attorney-client privilege protects: A communication. Between privileged persons (attorney, client, or in some cases, an agent) Made in confidence.
How is attorney client privilege waived?
Attorney-client privilege is waived by disclosing the substance of the communication to a third party. Waiver can be voluntary or involuntary (accidental).
What are some examples of legal functions?
Examples of legal functions: Advising company on existing law. Analyzing conduct for conformity with law or judgments regarding law. Advising on imminent litigation.
When discussing legal matters, should meeting minutes indicate clearly that?
In board meetings, conference calls and other meetings: When discussing legal matters, Board meeting minutes should indicate clearly that: In-house counsel attended in his/her role as legal advisor. Discussions were for the purpose of providing legal advice. Discussions were confidential and intended to be privileged.
Is communication between counsel and a public relations firm privileged?
Ordinarily, communication between counsel and a public relations/crisis management firm is not considered privileged unless the party asserting the privilege can show that the communication was necessary for the client to obtain informed legal advice.
Who can exclude from privileged discussions?
Consider excluding from privileged discussions any observer or third party whose presence may prevent a claim to privilege (investment bankers, auditors, consultants).
Is an investigative report privileged?
An investigative report that is sent to an attorney or even authored by an attorney must still be primarily or predominantly of a legal character to be privileged. Under most circumstances, production of information to the Government waives privilege as to that information in subsequent civil suits.
What is attorney-client privilege?
The attorney-client privilege applies in limited circumstances, in particular: Requests for legal advice from a client to an attorney. Requests for information from an attorney for information needed to formulate or provide legal advice. The legal advice is actually given by the attorney.
What is the most important thing to do to protect the privilege of attorney?
There are several things you (and your business colleagues) can do to ensure the best possible outcome with respect to protecting the privilege: The most important thing you can do is to be sure to properly label communications that meet the test for attorney-client communications.
Is it privileged to label something?
First, labeling something privileged does not make it privileged. It depends on whether the communication is for the purposes of obtaining or receiving legal advice.
Can you discuss privileged information with your spouse?
Likewise, as much as you love your spouse or significant other, you cannot discuss privileged information with him or her. And, as noted above, the more people in the loop on privileged communications the greater the chance that someone trips up on the confidentiality prong.
Do you have to keep legal advice confidential?
You must keep legal advice confidential. It is absolutely critical that you and the company keep legal advice confidential. It cannot be passed along outside that company– a common problem with business colleagues who do not understand the problems doing so can cause.
Do you need to be vigilant when giving legal advice?
You need to be constantly vigilant regarding the scope of your communications with the business and understand when you are or are not giving legal advice and, if you are, that you take the extra step to clearly note in the communication that you are providing legal advice.
Is legal advice privileged?
Legal advice is broader than just litigation-related communications, i.e., it covers all legal advice including transactional and regulatory. Business advice, however, is never privileged, and – for in-house counsel in particular – the line between the two can appear blurry.
When to use attorney-client privilege?
The attorney-client privilege may be used when a complaint involves serious concerns (including potential criminal claims), may develop into a lawsuit, or may have the potential to impact a large number of employees (e.g., class action status), among other considerations. It is always best to contact your legal department in advance of launching an investigation when you suspect that the gravity of the situation may give rise to significant liability. So be sure to discuss upfront whether your in-house counsel or outside defense attorney wants any particular emails or document exchanges protected. Further, if you have any question whether or not you should be invoking the attorney-client privilege, always err on the side of caution and protect the documentation trail as much as possible.
What is the rule for a lawyer-client privilege?
Rule 1: Address communications to your attorney. This could be your in-house counsel or outside counsel, but for the attorney-client privilege to become effective, it must be addressed to an attorney who is providing legal advice and counsel. The privilege does not protect communications between workers when no attorney is present. In other words, you can't send an email to your non-attorney boss and mark it "privileged and confidential" because without an attorney on the receiving end to provide legal analysis and advice, there's no mechanism to protect the communication from legal discovery.
What is the rule for copying a document?
Rule 4 : Copy only a limited number of people who have a legitimate need to know the information. Do not copy or share the document with others, or the privilege may be lost. After all, if you copy 15 people on the communication, a court will likely infer that it wasn't all that confidential or proprietary to begin with.
What is business legal 101?
While you may hope that you never need them, it's wisest to bring yourself up to speed with certain elements of "Business Legal 101" to protect yourself and your company from unwanted legal exposure.
Is attorney client communication privileged?
Again, not all attorney-client communications will be deemed privileged once submitted in court, so always proceed with caution and continue to communicate in writing as if your document may be used as evidence in court at some point and blown up and placed in front of a jury.
Does SHRM offer legal advice?
SHRM provides content as a service to its readers and members. It does not offer legal advice, and cannot guarantee the accuracy or suitability of its content for a particular purpose. Disclaimer
Can a court overturn a document that is privileged?
Just because you mark a document "Privileged and Confidential" doesn't mean that a plaintiff's attorney won't challenge the privilege and that a court won't overturn it. Therefore, let caution rule the day when it comes to exchanging emails, documents, or other electronic communications that you mark privileged.
What is the attorney-client privilege?
The Attorney-Client Privilege. The attorney-client privilege may protect a communication from disclosure if five fundamental elements exist: (1) an attorney; (2) a client; (3) a communication; (4) a confidentiality that was anticipated and preserved; and (5) legal advice or assistance (as opposed to business or personal advice) ...
Where to put "privileged" in a document?
Likewise, a well-intentioned employee concerned about confidentiality may insert the word “Privileged” at the top of a document or communication so that it remains confidential. However, unless the nature of the communication is legal advice or it is a document prepared at the request of counsel in anticipation of litigation, the privilege does not apply.
What happens if an attorney withholds documents?
At the same time, if an attorney is overly restrictive or indiscriminately withholds documents, they risk losing credibility with opposing counsel and the court, which can make it more difficult to assert the privilege when necessary.
Why is an email not privileged?
However, if an email between outside and internal counsel is forwarded to someone outside of the legal team within the company, privilege is not broken because the communication is still between attorney and client.
When does the privilege apply?
The privilege likely only applies when that person is acting in a legal capacity. The determination of who is counsel is also more difficult with regard to corporate communications. In certain jurisdictions and situations, the privilege may include paralegals and assistants in the legal department.
When should non-lawyer communications be withheld?
The trickier question is whether the communication should be withheld or redacted when non-lawyers discuss, not legal advice they have been given, but legal advice they intend to seek from in-house counsel. The privilege analysis with non-lawyer communications becomes even more complicated when the work product doctrine is taken into consideration. Under the work product doctrine, communications and documents can be privileged even if the communication does not directly include or reference an attorney, if the work or communication was done at the direction of an attorney and in anticipation of litigation.
Is attorney client privilege in corporate email?
The applicability of the attorney-client privilege in the corporate environment is often most difficult to determine in the context of email, a now ubiquitous form of communication that frequently makes up the bulk of documents produced in discovery. Corporate emails often involve multiple people with long chains of multiple communications and attachments.
What is attorney client privilege?
The attorney-client privilege is one of the more complicated yet most respected areas of legal practice and covers oral and written communications to, from or with an attorney for the purpose of requesting or receiving legal advice. The attorney-client privilege protects certain communications from disclosure to third parties. To qualify for this protection, these communications must be confidential, between an attorney and client, and made for the purpose of obtaining or providing legal advice. The communication is not privileged if these three elements are not met. The overall purpose of this privilege is to encourage open dialogue and sharing of information to obtain legal advice without fear of disclosure to unintended parties.
Why is confidentiality important in attorney client privilege?
Despite the complex nature of attorney-client privilege application, confidentiality is a critical element for maintaining the privilege — specifically, the oral or written communication must be kept confidential for the privilege to apply. The privilege may be extinguished if the substance of the communication is disclosed or accessible to internal staff not directly involved in the matter or individuals outside of the corporation.
What is the case of Garvey v. Hulu?
Consider, for example, Garvey v. Hulu, LLC, a discovery dispute involving confidentiality concerns regarding internal access at Hulu to Jira system tickets. The defendant redacted content on Jira tickets where Hulu employees directly asked their in-house counsel for legal advice on a matter. The court rejected the plaintiff's argument that "confidentiality was destroyed by the fact that the Jira system is generally accessible to Hulu employees beyond those immediately participating in [the Jira] tickets.” The court highlighted the fact that only Hulu employees had access to the privileged communication and confidentiality was not destroyed by the possibility that other Hulu employees, not directly participating on those tickets, could have accessed them. It also noted that “material need not be kept under lock and key to remain confidential.”
What is acceptable use policy?
Many companies use Acceptable Use Policies that inform users that they essentially have no expectation of privacy in corporate systems. However, these policies should carve out an exception for legal advice from attorneys and other confidential communications. If your handbook and AUP inform all employees that the company may monitor any usage on its system, then it may be more difficult to claim confidential communications in certain instances. Your information classification policy should specifically include a confidential tab that covers privileged communications. Take care to label documents and emails appropriately. There are also some companies that start meetings with disclaimers about the communication that is probably about to take place.
Why do companies use Bring Your Own Device?
On the surface, bring-your-own-device policies appear to lower company costs, they present a number of hidden costs, including problems associated with attorney-client privilege. In a BYOD environment, companies have less control over the devices and are limited in their ability to build in adequate protection. In addition, companies have less control over information accessibility and how it is transmitted and stored on personal devices, which is potentially problematic from a confidentiality and attorney-client privilege perspective.
What is the need to maintain a balance between privileged discussions in the office and societal interest in effectively prosecuting
Historically, society has accepted the need to maintain a balance between privileged discussions in the office on one hand versus societal interest in effectively prosecuting corporate malfeasance on the other hand. Technological advancement adds a complicating factor forcing privilege’s risk landscape to shift and evolve considering various ways to communicate, including texting, agile project management platforms, instant messaging and video communication systems.
Is privilege a clear cut process?
The application of privilege is not a clear-cut process, particularly given jurisdiction considerations. For example, privilege application is even more complex for multinational corporations, where the concept of privilege for in-house counsel is either limited in some countries or does not exist at all (and engagement of outside counsel, such as a hired firm, may be needed to help preserve the privilege in other jurisdictions).
Do attached documents constitute pre-existing business documents?
These and other ambigious or confusing decisions highlight the wisdom of corporate employees seeking legal advice about their draft documents articulating this context in their transmittal communications — confirming that the attached documents do not constitute pre-existing ordinary business documents, but are instead newly-created draft documents about which the employees require legal advice.
Does the attorney-client privilege protect pre-existing business documents?
The attorney-client privilege rarely, if ever, protects pre-existing business documents that corporate employees send to their corporate employer's lawyer. However, the privilege can clearly protect draft business documents that such employees and their lawyers jointly prepare (as long as the drafts reflect lawyers' legal advice rather than business, stylistic, or grammatical advice, etc.). Surprisingly, some decisions have trouble distinguishing between these two scenarios.

“But In-House Counsel Was Copied on The Email, Isn’T That Enough?”
The Attorney-Client Privilege
- The attorney-client privilege may protect a communication from disclosure if five fundamental elements exist: (1) an attorney; (2) a client; (3) a communication; (4) a confidentiality that was anticipated and preserved; and (5) legal advice or assistance (as opposed to business or personal advice) as the primary purpose of the communication. Paul R...
In-House Counsel and The Attorney-Client Privilege
- The nature of many business communications makes it difficult to determine when the attorney-client privilege applies. Business communications often involve many participants, outside or in-house counsel may or may not be personally involved, legal recommendations or requests are often mixed with day-to-day correspondence and long email chains meander along multiple topi…
Who Is The Attorney and Who Is The Client?
- Communications with outside counsel are often easy to segregate and identify. If Company A hires Law Firm B to litigate a dispute, it is clear that communications between Company A and Law Firm B are likely protected by the attorney-client privilege (and often the work product doctrine as well). However, the application of the attorney-client privilege is more nuanced with i…
Is The Communication Intended to Be Confidential?
- The applicability of the attorney-client privilege in the corporate environment is often most difficult to determine in the context of email, a now ubiquitous form of communication that frequently makes up the bulk of documents produced in discovery. Corporate emails often involve multiple people with long chains of multiple communications and attachments. In making a privi…
Is Legal Advice The Primary Purpose?
- It may be tempting for a privilege reviewer to quickly mark as privileged a communication between in-house counsel and the client or a document that has boilerplate language indicating that the communication is privileged. However, privilege is not that simple. The communication must satisfy all privilege requirements, including the requirement that the communication’s “pri…
Popular Posts:
- 1. who is the department of justice attorney general
- 2. how to label an attorney retired on letterhead
- 3. my sibling who has power of attorney lives out of state but i take care of my parents
- 4. how to file complaint against district attorney
- 5. why you should have living will and a power of attorney
- 6. who do i report abuse of power of attorney to
- 7. how to terminate attorney client agreement
- 8. how can i find out who my dads attorney is
- 9. where is attorney richard isacoff?
- 10. how to make a claim against an attorney bond